Glossary of terms
-

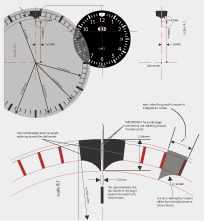
-
Glossary
Analog
Analog watches display time using hands sweeping in position above a dial face. They may use combinations of dials, dial rings, and sub-dials.
Bezel
A watch bezel is the ring that surrounds the face/crystal of the watch and may hold the crystal in place. The bezel is used for decorative or functional purposes and may be fixed or moveable.
Case
The watch case is the main body that houses and protects the watch parts from dust, dampness and shocks.
Caseback
The caseback attaches to the back of the watch case. It is screwed on using threads around its circumference mating with threads in the case, or it can be held on using screws. The caseback allows access to the internal components, such as the movement and battery.
Chronograph
A watch with two or more independent time systems. One indicates the time of the day and the other measures intervals of time. Typically, pushers in the case manipulate the timing function and is displayed using sub-dials or a digital display on the watch face.
Crown
The crown or winding button is used to set and/or wind the watch. It is affixed to the end of the winding stem and is typically screwed down or pushed down. On a quartz watch, the crown is used to set the hands and date. On a mechanical watch, the crown is used to set the hands, date, and may also wind the mainspring. A screw down crown is used to make a watch more water resistant.
Crystal
The crystal is the transparent cover over the watch face. Watch crystals are made of different materials with the three most common being Sapphire glass, mineral glass, and plastic.
DLC
Diamond Like Carbon is a carbon coating that provides toughness and wear resistance to our stainless steel watches. These coatings exhibit a desirable combination of a low coefficient of friction and high micro-hardness.
GMT
Greenwich Mean Time abbreviation. The GMT time system originally refers to solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, which was adopted as a global time standard. GMT is used as a common time reference in aviation (Zulu time) and was originally used by mariners.
Lug
The lugs protrude from the watch case and are used to attach the strap or bracelet. The dimension between two lugs on the same side of the case determine the strap size, i.e. 20 mm.
Movement
The mechanism inside the case that keeps time and moves the hands, calendar, and other complications. Movements are either mechanical or quartz.
Movement—Mechanical
The mechanical apparatus that uses springs, gears, and wheels acting in unison to keep time and move the hands, calendar and other complications. Mainspring force is the power source which acts upon the other mechanical components. The mainspring is wound by the crown or by accelerations from movement. The self-winding watch contains an eccentric weight, known as the rotor, which turns on a pivot and is attached to a ratcheted winding mechanism. The normal motion of the wearer's arm cause the rotor turn around its pivot, thus winding the mainspring.
Movement—Quartz
An electronic apparatus that uses a quartz resonator for the time base. It typically uses a battery as the power source acting on electromechanical components. Quartz movements can be extremely accurate due to their steady oscillation characteristic.
Pusher
A button that makes mechanical contact with the movement to affect an action. For example, a chronograph watch uses pushers to start and stop the action of the timer.
Sapphire Crystal
The Sapphire crystal is the most scratch resistant crystal available. It is the hardest substance next to a diamond and highly resistant to scratching and abrasion (9 Mohs scale). It is approximately three times harder than mineral crystals and twenty times harder than acrylic crystal.
Sub—dial
A small dial on the watch face used for various purposes, such as chronograph timing or indicating the date.
Water Resistance
The water resistance of a watch is tested by its ability to resist the penetration of water. Water pressure is measured in bar with 1 bar being equivalent to 1 atmosphere. Water resistance is increased by employing a screw down crown.
